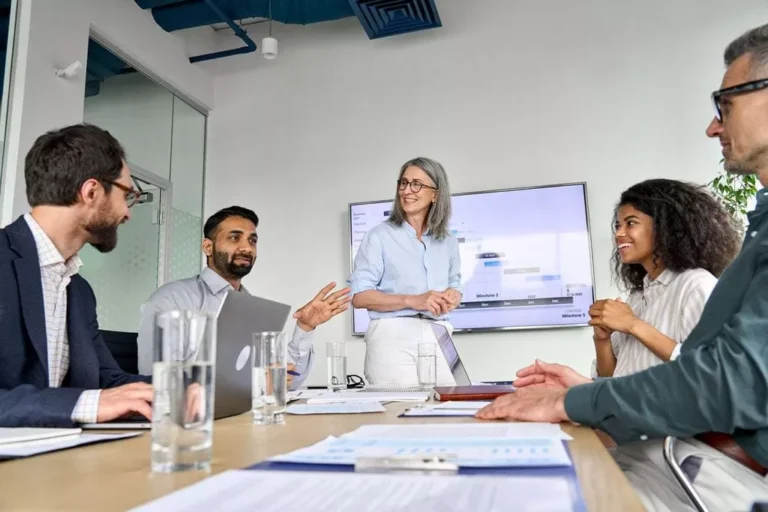
Today, merchant banks play a crucial role in the Indian financial market, offering a wide array of services that cater to the complex needs of modern businesses. Merchant banking, a critical financial services industry segment, plays a pivotal role in fostering corporate growth and facilitating complex financial transactions. In India, merchant banks are essential in guiding businesses through mergers and acquisitions, underwriting, and providing advisory services, thereby contributing significantly to the nation’s economic development. These institutions serve as intermediaries between issuers and investors, providing specialized financial services that traditional banks do not offer.
Functions of Merchant Banks
Later, the ICICI set up its merchant banking division in 1973 followed by a number of other commercial banks like Canara Bank, Bank of Broada, Bank of India, Syndicate Bank, Punjab National Bank, Central Bank of India, UCO Bank, etc. Merchant banking services, in India, were started only in 1967 by National Grindlays. The State Bank of India was the first Indian commercial bank to set up a separate merchant banking division in 1972. In United Kingdom, Merchant Banks arrived in the late eighteenth century and early nineteenth century. Rich merchant houses which made their fortunes in a colonial trade diversified into banking.
How did the 1990s economic reforms change banking in India?
This initiative redirected funds from wealthy sectors to underprivileged communities, focusing on priority sector lending. Subsequent expansions reinforced the government’s commitment to social welfare through banking. The British colonial period established formal banking practices, initially serving colonial interests. Regulations limited indigenous banks’ growth, leading to the founding of the Reserve Bank of India in 1935, which implemented structured banking practices and accountability, ultimately impacting the sector’s resilience after independence. Once the banks were established in the country, regular monitoring and regulations need to be followed to continue the profits provided by the banking sector.
History of Banking in India
Merchant Banking activity was formally initiated into the Indian capital markets when Grind lays Bank received the license from Reserve Bank in 1967. Grind lays which started with management of capital issues, recognized the needs of emerging class of entrepreneurs for diverse financial services ranging from production planning and system design to market research. Apart from meeting specially, the needs of small-scale units it provided management constancy services to large and medium sized companies. The division took up the task of supporting new entrepreneur and existing units in the evaluation of new projects and raising funds through borrowing and issue of equity. Consequent to the recommendations of Banking Commission in1972, that Indian bank should start Merchant Banking Division in 1972. In the initial years the SBI’s objective was to render corporate advice and assistance to small and medium entrepreneurs.
She has spent a lot of time researching and writing about the ever-changing world of money-making games and websites, making her an expert at finding ways to make money online. Other banks also started these services such as PNB, Bank of India, UCO Bank, etc. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was given more authority to oversee and regulate the banking system. All these banks were later merged with the State Bank of India in 2017, except for the State Bank of Saurashtra, which merged in 2008 and State Bank of Indore, which merged in 2010. Candidates can check the list of Banking sector reforms and Acts at the linked article.
Deregulation and liberalisation of the industry in India has accounted for changes in the financial sector. With the passage of time merchant banking activities have changed in line with the changing need pattern of the enterprises in the wake of economic development. The merchant banker formal merchant banking activity in india was originated in primarily came into being as corporate counsellors for restructuring base of capital, thereafter for issue management and underwriting of the same. With the advent of the industrial boom in India, there has been a growing need of Merchant Bankers.
- Some of these deposits were lent to others, creating a primitive form of banking.
- Key regulations enacted during this period included the Currency and Bank Notes Act of 1926 and the Banking Regulation Act of 1949, which introduced licensing requirements, deposit protection, and auditing standards.
- The first bank of India was the “Bank of Hindustan”, established in 1770 and located in the then Indian capital, Calcutta.
- The need for specialized merchant banking services was felt in India with the rapid growth in the number and size of the issues made in the primary market.
Banking in India has undergone significant transformation over centuries, evolving from simple practices to a complex system of financial institutions. Ancient India relied on informal banking systems, with moneylenders providing financial services in local communities. These early systems centred around trust and relationships, catering primarily to the needs of agricultural and trade sectors.
Finally, the top players, which exist in merchant banking, are also dealt with their services are also been focused. To get the practical knowledge about merchant banking activities, the researcher visited and interviewed State bank of India, Kotak Mahindra bank and SPA Merchant Bankers Ltd. However, it was only in 1992 after the formation of Securities and Exchange Board of India that it is defined and a set of rules and regulations in place.
The Imperial Bank of India was later nationalised in 1955 and was named The State Bank of India, which is currently the largest Public sector Bank. Further below in this article, we shall discuss the different phases of Bank industry evolution. Project counselling which includes credit-syndication and the working capital. The first authoritative definition for the term ‘Merchant Banker’ has been given in the Rule 2 (e) of SEBI (Merchant Bankers) Rules, 1922.
The progress of any economy mainly depends on the efficient financial system of the country. The importance of the financial sector reforms affirms an efficient means for solving the problems of economic, financial and social in India and also where in the developing nations of the world. The progress of the Securities Industry of any country depends mainly on the flow of funds.
Compliance with these regulations is crucial for maintaining the integrity and stability of the financial system. Merchant banks are also subject to periodic inspections and audits by SEBI to ensure ongoing compliance. Any violations can result in penalties, including suspension or cancellation of the registration certificate. In 1969, the nationalisation of banks aimed to ensure credit availability in rural areas and promote economic equality.